Research
Thesis Papers
Scaling Robot Learning without Scaling Human Effort [thesis]
Master’s Thesis
Christofer Stephenson Memorial Award for Graduate Research: Best Master’s Thesis in Computer Science
Leveraging Affordance Representations for Robot Learning [thesis] [publication]
Undergraduate Honors Thesis
Conference Papers
* denotes equal contribution
Crossing the Human-Robot Embodiment Gap with Sim-to-Real Reinforcement Learning using One Human Demonstration [paper] [site]
Tyler Ga Wei Lum*, Olivia Y. Lee*, C. Karen Liu, Jeannette Bohg
Conference on Robot Learning (CoRL) 2025
TL;DR: Our real-to-sim-to-real framework trains dexterous manipulation policies with RL in simulation from a single RGB-D human video demonstration, which we deploy zero-shot on a real robot.
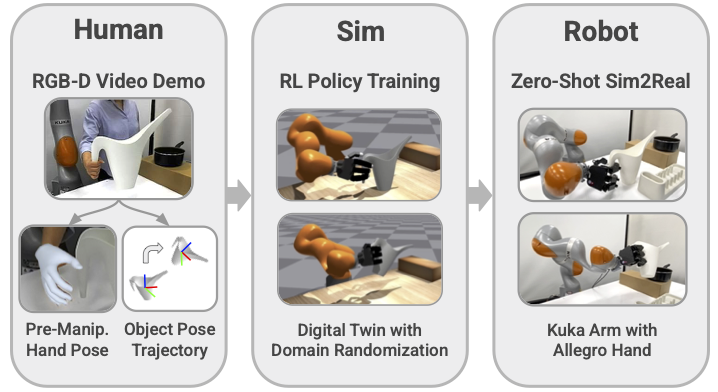
We present Human2Sim2Robot, a real-to-sim-to-real framework for training dexterous manipulation policies using only one RGB-D video of a human demonstrating a task. We leverage reinforcement learning (RL) in simulation to cross the human-robot embodiment gap without wearables, teleoperation, or large-scale data collection typically necessary for imitation learning methods. From the demonstration, we extract two task-specific components: (1) the object pose trajectory to define an object-centric, embodiment-agnostic reward function, and (2) the pre-manipulation hand pose to initialize and guide exploration during RL training. These eliminate the need for task-specific reward engineering. Human2Sim2Robot significantly outperforms baselines across a range of grasping, non-prehensile manipulation, and extrinsic manipulation tasks.
Tyler Ga Wei Lum*, Olivia Y. Lee*, C. Karen Liu, Jeannette Bohg
Conference on Robot Learning (CoRL) 2025
TL;DR: Our real-to-sim-to-real framework trains dexterous manipulation policies with RL in simulation from a single RGB-D human video demonstration, which we deploy zero-shot on a real robot.
We present Human2Sim2Robot, a real-to-sim-to-real framework for training dexterous manipulation policies using only one RGB-D video of a human demonstrating a task. We leverage reinforcement learning (RL) in simulation to cross the human-robot embodiment gap without wearables, teleoperation, or large-scale data collection typically necessary for imitation learning methods. From the demonstration, we extract two task-specific components: (1) the object pose trajectory to define an object-centric, embodiment-agnostic reward function, and (2) the pre-manipulation hand pose to initialize and guide exploration during RL training. These eliminate the need for task-specific reward engineering. Human2Sim2Robot significantly outperforms baselines across a range of grasping, non-prehensile manipulation, and extrinsic manipulation tasks.
Affordance-Guided Reinforcement Learning via Visual Prompting [paper] [site]
Olivia Y. Lee, Annie Xie, Kuan Fang, Karl Pertsch, and Chelsea Finn
IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) 2025
Robotics Science and Systems (RSS), 2024 Workshops: Task Specification & Lifelong Robot Learning
TL;DR: To effectively improve the performance of policies pre-trained on diverse data, we make fine-tuning with online RL more efficient using affordance representations extracted from VLMs zero-shot.
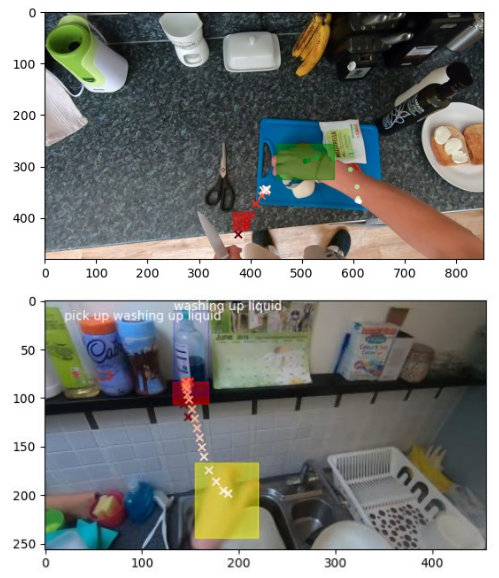
We present an approach that extracts affordance representations from VLMs via keypoints to define dense shaping rewards for online reinforcement learning. We pretrain policies on Bridge data and a modest number of in-domain demonstrations of the task, and finetune policies online using VLM-generated dense rewards. On a real-world manipulation task, our VLM-generated rewards improve the sample efficiency of autonomous RL, enabling task completion in 20K online finetuning steps. Our approach is robust to reducing in-domain demonstrations used for pretraining, reaching comparable performance in 35K online finetuning steps.
Olivia Y. Lee, Annie Xie, Kuan Fang, Karl Pertsch, and Chelsea Finn
IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) 2025
Robotics Science and Systems (RSS), 2024 Workshops: Task Specification & Lifelong Robot Learning
TL;DR: To effectively improve the performance of policies pre-trained on diverse data, we make fine-tuning with online RL more efficient using affordance representations extracted from VLMs zero-shot.
We present an approach that extracts affordance representations from VLMs via keypoints to define dense shaping rewards for online reinforcement learning. We pretrain policies on Bridge data and a modest number of in-domain demonstrations of the task, and finetune policies online using VLM-generated dense rewards. On a real-world manipulation task, our VLM-generated rewards improve the sample efficiency of autonomous RL, enabling task completion in 20K online finetuning steps. Our approach is robust to reducing in-domain demonstrations used for pretraining, reaching comparable performance in 35K online finetuning steps.
Play it by Ear: Learning Skills amidst Occlusion through Audio-Visual Imitation Learning [paper] [site] [publication]
Maximilian Du*, Olivia Y. Lee*, Suraj Nair, and Chelsea Finn
Robotics Science and Systems (RSS), 2022 [recording]
TL;DR: We show that augmenting image input with audio and proprioception, as well as online human interventions, help imitation learning policies succeed on challenging partially-occluded tasks.
We present a system that learns to complete partially-observed manipulation tasks by reasoning over vision, audio, and memory. We combine offline imitation learning from a modest number of tele-operated demonstrations and online finetuning with human interventions. In simulation, our system benefits from using audio and online interventions, which improve success rates of offline imitation learning by ~20%. On a Franka Emika Panda robot, our system completes manipulation tasks under occlusion with a 70% success rate, 50% higher than a policy that does not use audio.
Maximilian Du*, Olivia Y. Lee*, Suraj Nair, and Chelsea Finn
Robotics Science and Systems (RSS), 2022 [recording]
TL;DR: We show that augmenting image input with audio and proprioception, as well as online human interventions, help imitation learning policies succeed on challenging partially-occluded tasks.
We present a system that learns to complete partially-observed manipulation tasks by reasoning over vision, audio, and memory. We combine offline imitation learning from a modest number of tele-operated demonstrations and online finetuning with human interventions. In simulation, our system benefits from using audio and online interventions, which improve success rates of offline imitation learning by ~20%. On a Franka Emika Panda robot, our system completes manipulation tasks under occlusion with a 70% success rate, 50% higher than a policy that does not use audio.

